The Effects Of Insomnia On The Brain

These brain areas had also recently.
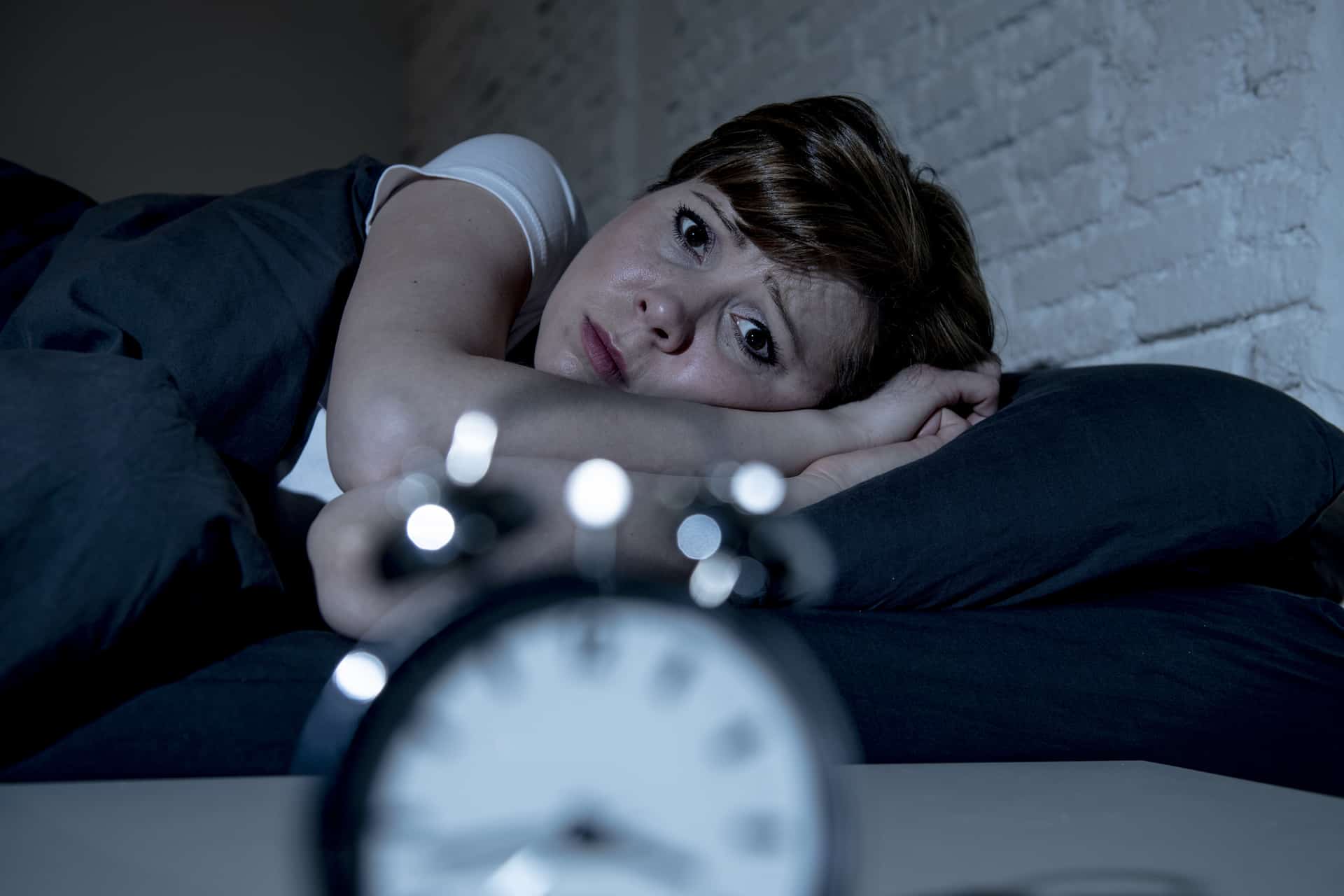
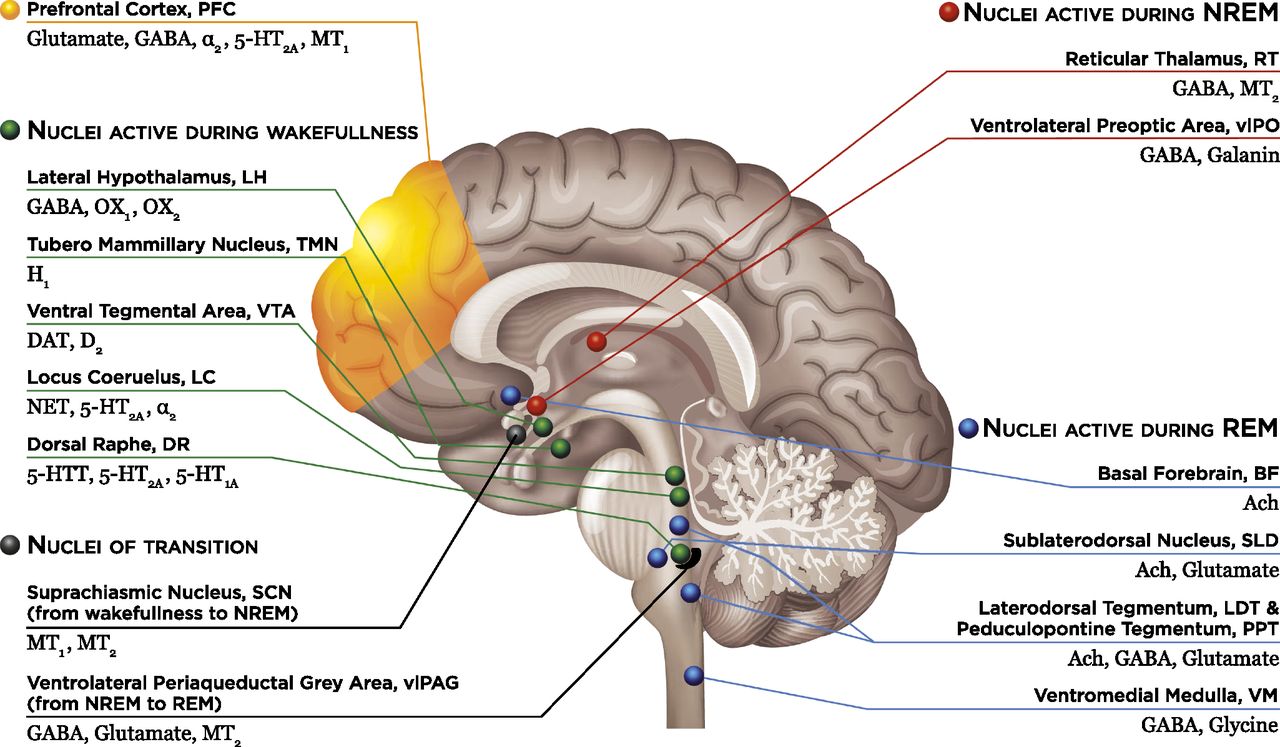
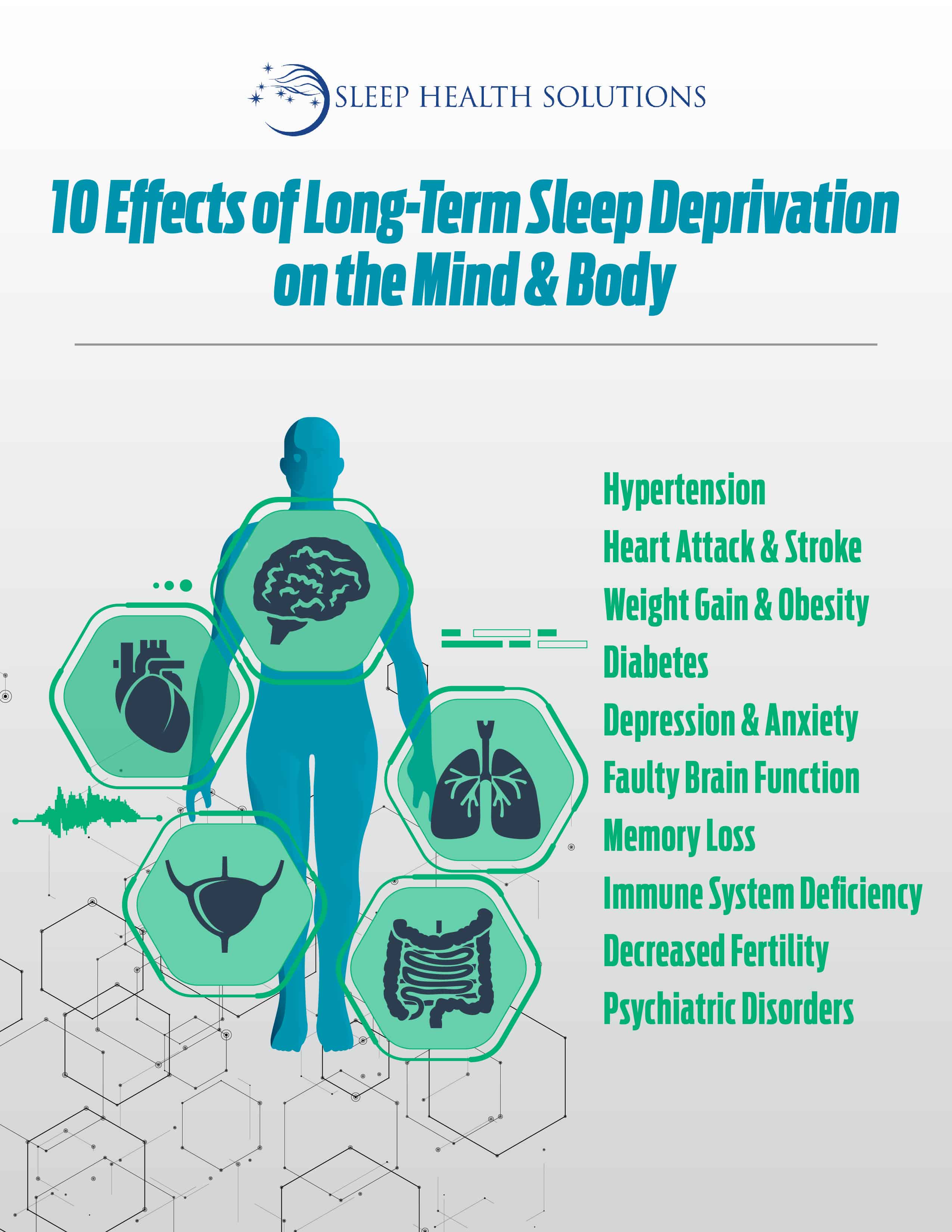
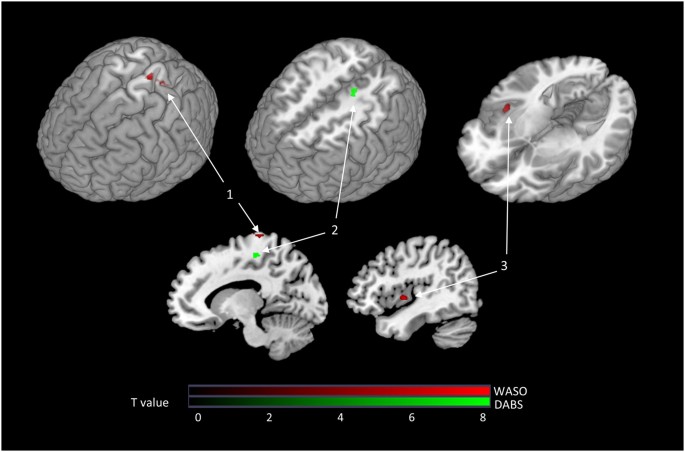
The effects of insomnia on the brain. The long term effects of sleep deprivation are real. Science has linked poor slumber with a number of health problems. Another significant part of the insomnia risk genes was active in specific cell types of parts of the frontal cortex and the subcortical nuclei of the brain. Complications of insomnia may include.
In addition people with insomnia may have problems turning off. Adults can take between 1 and 5 milligrams an hour before. It drains your mental abilities and puts your physical health at real risk. 19 alterations in sleep microstructure which are suspected in individuals with insomnia 20 may also influence cognitive performance.
Other risks of a sleep deprived brain are hallucinations mania impulsive behavior depression paranoia and suicidal thoughts. Higher melatonin levels make you feel sleepier but too much can disrupt your sleep cycle and cause headaches nausea and irritability. Lower performance on the job or at school slowed reaction time while driving and a higher risk of accidents mental health disorders such as depression an anxiety disorder or substance abuse. These factors may require distinct treatment mechanisms.
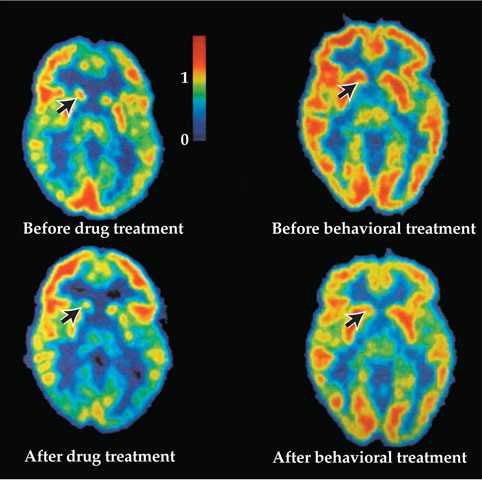
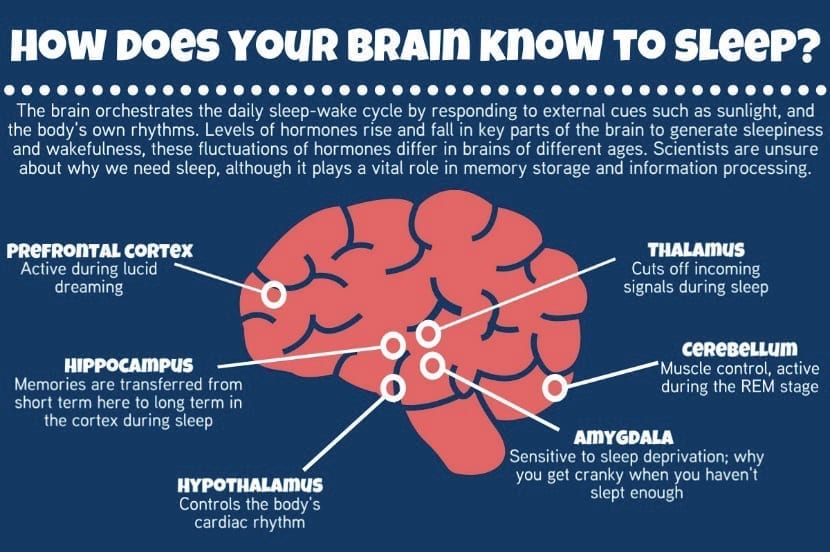
People with insomnia may have intact homeostatic and circadian function for example but abnormal metabolism in the brain s resting state networks during sleep said daniel j. The ucsf study showed that poorer sleep quality such as sleep quality among patients with chronic insomnia is associated with total cortical and regional frontal lobe matter volumes which causes cognitive deficits in attention executive function and nonverbal memory. Some of the effects that insomnia can have on the brain include the inability to concentrate stifled creativity short and long term memory loss and mood swings.














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/multiple-sclerosis-and-insomnia-diagnosis-and-treatment-2440627_v2-869acf8f5f4049eb82dd679686f5adb4.png)